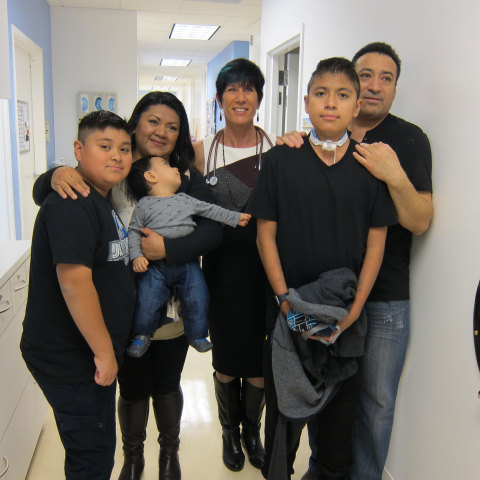
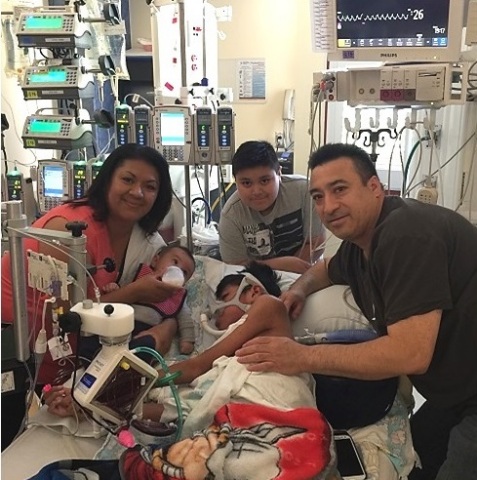
PALO ALTO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--2016 is starting off a whole lot better than last year for 14-year-old Oswaldo Jimenez of Salem, Oregon.
Last year at this time, he was sick. Life-threateningly sick. Diagnosed with pulmonary arterial hypertension at age 9, his heart and lungs were failing, and a heart-lung transplant seemed to be his only real hope for survival.
Oswaldo was referred to doctors at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital Stanford and Stanford Children’s Health, one of America’s leading centers for organ transplant. His doctors at Packard Children’s determined that Oswaldo would indeed need a transplant, but that he could return home to Oregon and await the call for transplant there. But in the spring, Oswaldo’s condition rapidly worsened, and he was admitted to a local hospital and emergency airlifted to Packard Children’s in May.
What happened? The pulmonary arterial hypertension made it hard for blood to flow properly through Oswaldo’s lungs, where blood picks up oxygen for the rest of the body. “The high blood pressure in his lungs was requiring his heart to pump harder and harder,” explained pediatric cardiologist Jeffrey Feinstein, MD, director of the Vera Moulton Wall Center for Pulmonary Vascular Disease, and head of the hospital’s pediatric pulmonary hypertension program. “This eventually caused his heart to fail.”
“When we initially evaluated him a few months earlier, he had very few symptoms; when he returned, he could only walk a short distance before getting breathless,” added Feinstein, who is also a professor of pediatrics at the Stanford School of Medicine and the Dunlevie Family Professor of Pulmonary Vascular Disease. “The pressure in his lungs also caused two episodes of pulmonary hemorrhage. This bleeding into the lungs can be fatal.”
Combined heart and lung transplants are so rare that only 24 were performed in the United States in 2014. Stanford has long been a national leader in multi-organ transplantation, performing the world’s first successful combined heart-lung transplant, on an adult, at Stanford Hospital in 1981.
Listing Oswaldo for transplant was just the beginning. Care teams wanted to ensure his failing heart and lungs could keep going until donor organs were available. They needed to establish what is referred to as a “bridge-to-transplant” solution, one that would sustain Oswaldo’s organs until transplant could occur.
A creative but risky way to keep Oswaldo moving
“An integral element to success for children awaiting lung transplants is to keep them moving around,” said pediatric pulmonologist Carol Conrad, MD, director of the pediatric lung and heart-lung transplant program at the hospital and an associate professor of pediatrics at the School of Medicine. “Being in good shape helps to make them good candidates for the transplant operation. Pre-operative debilitation leads to prolonged recovery period post-op and a poorer outcome in the long run.”
It was then that doctors decided to try a novel procedure, one that would enable Oswaldo to be mobile. Called a pulmonary artery to left atrial shunt, it was a surgery that had been used only a dozen times in patients nationwide. The surgery would reduce the workload on his failing heart, and allow Oswaldo to stay mobile and help oxygenate his blood while awaiting transplant.
“He was so critically ill and it was a very risky procedure; he was at high risk of cardiac arrest when being put to sleep for the surgery,” said Katsuhide Maeda, MD, surgical director of lung and heart-lung transplant program and a clinical assistant professor of cardiothoracic surgery at the School of Medicine. “But essentially, this shunt established a ‘lung’ that served to oxygenate his blood as it flowed through a box outside of his body. Since the device was reasonably small, it allowed him to stay awake and mobile while awaiting transplant.”
For parents Carmen Hernandez and Martin Jimenez, it was a difficult decision to go forward with this novel procedure, but there were no other options — and they trusted the team.
“We weren’t given any hope until we came here,” said Oswaldo’s mother, Carmen Hernandez, via a translator. “This seemed to give him the best chance to live.”
How it’s done
The procedure involved the insertion of a tube that redirected blood away from Oswaldo’s lungs into the oxygenator. This, in turn, provided oxygen to the blood and then returned it to his body, with his own heart providing the pump. Reports on this shunt device being able to sustain patients’ lives range from several weeks to six months, depending mostly on being able to prevent the blood from clotting while avoiding complications such as bleeding or stroke.
On July 12, Oswaldo made history by becoming the first child in the western United States to undergo this treatment — it saved his life and bought him time. Then, just one week after receiving the shunt, donor organs became available. Oswaldo received his heart and lung transplant on July 19.
“We are so, so thankful for organ donation,” said mom, Carmen. “During another family’s time of incredible grief, they gave my son the ultimate gift of life.”
Looking Ahead
The post-operative period was complicated, but now Oswaldo and his family just recently returned home to Oregon in late December. “He’s steadily improving,” said Conrad, “he’s been weaned off his ventilator and so we removed the trach (breathing tube). We expect to see him return to many of his normal activities over the next few months.”
“There are no words to express our gratitude and we can’t say enough about our medical team,” said dad, Martin. “Once we arrived here, we knew we had the best and most experienced care possible.” Added Carmen, “Now, the doctors can use this therapy to treat other patients. Maybe the next family faced with this won’t have such a hard decision to make, because it certainly worked for Oswaldo.”
Conrad says they will likely use this bridge-to-transplant treatment again, adding yet another option to the Stanford Medicine therapies and innovations for kids with failing hearts and lungs.
For Oswaldo, he is simply looking forward to being a kid again. “I want to run and play, and get my life back,” he said, proud that he made history as the first kid on the West Coast to receive this treatment. As far as what the future holds?
“I just know I want to do something big in life.” We think he already has.
About Stanford Children’s Health and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford
Stanford Children’s Health, with Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at its core, is the largest Bay Area health care enterprise exclusively dedicated to children and expectant mothers. Long recognized by U.S. News & World Report as one of America’s best, we are a leader in world-class, nurturing care and extraordinary outcomes in every pediatric and obstetric specialty, with care ranging from the routine to rare, regardless of a family’s ability to pay. Together with our Stanford Medicine physicians, nurses, and staff, we can be accessed through partnerships, collaborations, outreach, specialty clinics and primary care practices at more than 60 locations in Northern California and 100 locations in the U.S. western region. As a non-profit, we are committed to supporting our community – from caring for uninsured or underinsured kids, homeless teens and pregnant moms, to helping re-establish school nurse positions in local schools. Learn more at stanfordchildrens.org and on our Healthier, Happy Lives blog. You can also discover how we are Building the Hospital of the Future. Join us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and YouTube.