HAYWARD, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Alphabet Energy, the global leader in thermoelectrics for waste heat to power (WHP) and Heat is Power, the trade association for the WHP industry today released statistics in time for the Paris Climate Change Conference (COP21) to help explain just how valuable waste heat can be in generating clean electricity and reducing emissions.
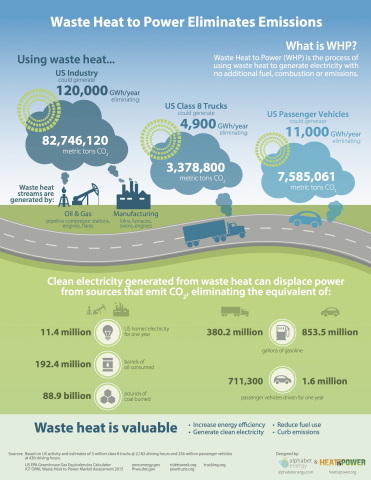
Solar and wind have made excellent progress in paving the way for a low-carbon path, but both are limited by low capacity factors resulting from their intermittent nature, producing power only when the sun shines or the wind blows. Waste heat to power is the process of converting exhaust heat into electricity without additional fuel or emissions. Regardless of time of day or wind speed and direction, energy-intensive industries, such as oil & gas operations, industrial manufacturing and transportation, operate around the clock, year-round, and produce enough waste heat to generate over 15 GW of electricity per year, according to ICF and Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
While WHP is an emerging technology and installed capacity is not yet on par with that of solar and wind, estimates show that to generate nearly 52,000 GWh of electricity, it takes 22.7 GW of solar compared to only 6.5 GW of WHP due to WHP’s much greater capacity factor. In the U.S. industrial sector alone (e.g., oil & gas, industrial manufacturing), WHP technologies could generate over 120,000 GWh/year of electricity, more than double the nearly 52,000 GWh/year that could be generated from the 22.7 GW capacity for the entire U.S. photovoltaic market (based on a 25.9 percent capacity factor). See the table below for an example analysis.
|
U.S. Renewable |
U.S. Installed |
Average Capacity |
Electricity Generated |
|||
| Wind | 69.47 GW | 34.0% | 207,000 GWh | |||
| Solar | 22.7 GW | 25.9% | 51,500 GWh | |||
| WHP |
15.265 GW
(potential, |
90.0% | 120,300 GWh | |||
|
Sources: US DOE NREL, SEIA, ICF/ORNL, US EIA |
||||||
“Waste heat to power could have as big an impact on carbon reduction as solar, but much more quickly,” said Matt Scullin, founder and CEO, Alphabet Energy. “Waste heat from furnaces, engines, flares, compressor stations and vehicle tailpipes is abundant throughout the U.S. industrial sector and on our highways. With a much higher capacity factor than wind and solar, the U.S. industrial sector could convert its waste heat into over 120,000 GWh of clean electricity per year. That’s enough electricity to power Norway for an entire year, while also eliminating nearly 100 million metric tons of CO2. WHP is a path to tackling an entire climate mitigation wedge of 1 billion tonnes of CO2 by 2050.”
In the U.S., both House and Senate legislators have introduced the Power Efficiency and Resiliency (POWER) Act that would add waste heat to power to the list of renewable technologies that qualify for the 30 percent federal investment tax credit. More government efforts worldwide can help drive adoption.
For more information, please view the Waste Heat to Power infographic or Matt Scullin’s recent blog post, Waste Heat to Power as a Carbon Stabilization Wedge.
About Alphabet Energy
Alphabet Energy makes waste heat valuable. Leveraging nanotechnology research from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Michigan State University, and with over 60 patents issued and filed, the company’s proprietary PowerBlocks™ thermoelectric material turns waste heat from exhaust into electricity and serves as the technology platform for the company’s line of waste heat recovery products, including the E1™ Thermoelectric Generator and PowerModules™. Customers in energy-intensive industries from oil & gas, mining, manufacturing, transportation, to defense use Alphabet Energy’s products to generate reliable remote power while also reducing fuel consumption, operating costs and carbon emissions. Learn more at www.alphabetenergy.com or on social media:
- twitter.com/alphabetenergy
- linkedin.com/company/alphabet-energy
- facebook.com/alphabetenergy
- instagram.com/alphabetenergy
- pinterest.com/alphabetenergy